The Instrumentation, Systems, and Automation Society (ISA) is one of
the leading process control trade and standards organizations. The ISA
has developed a set of symbols for use in engineering drawings and
designs of control loops (ISA S5.1 instrumentation symbol
specification). You should be familiar with ISA symbology so that you
can demonstrate possible process control loop solutions on paper to
your customer.
IDENTIFICATION LETTERS
Identification letters on the ISA symbols (e.g., TT for temperature
transmitter) indicate:
The variable being measured (e.g., flow, pressure, temperature)
The device’s function (e.g., transmitter, switch, valve, sensor,
indicator)
Table 7.1 on page 26 shows the ISA identification letter designations.
The initial letter indicates the measured variable. The second letter
indicates a modifier, readout, or device function. The third letter
usually indicates either a device function or a modifier.
For example, “FIC” on an instrument tag represents a flow indicating
controller. “PT” represents a pressure transmitter. You can find
identification letter symbology information on the ISA Web site at
http://www.isa.org.
TAG NUMBERS
Numbers on P&ID symbols represent instrument tag numbers. Often
these numbers are associated with a particular control loop

Figure 7.5 shows a control loop using ISA symbology.
Drawings of this kind are known as piping and instrumentation
drawings (P&ID).
SYMBOLS
In a P&ID, a circle represents individual measurement instruments,
such as transmitters, sensors, and detectors (Figure 7.6).
A single horizontal line running across the center of the shape
indicates that the instrument or function is located in a primary
location (e.g., a control room). A double line indicates that the
function is in an auxiliary location (e.g., an instrument rack). The
absence of a line indicates that the function is field mounted, and a
dotted line indicates that the function or instrument is inaccessible
(e.g., located behind a panel board).
A square with a circle inside represents instruments that both display
measurement readings and perform some control function
(Figure 7.7). Many modern transmitters are equipped with
microprocessors that perform control calculations and send control
output signals to final control elements.
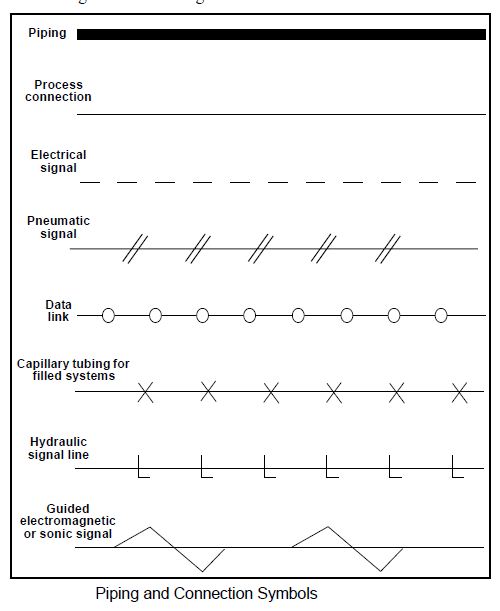
Piping and Connections
Piping and connections are represented with several different symbols





















0 comments:
Post a Comment